"Digital screening may divert lower-risk individuals to online options and offer acceptable alternatives for higher-risk non-responders, suggesting a mixed-modality approach may enhance uptake."
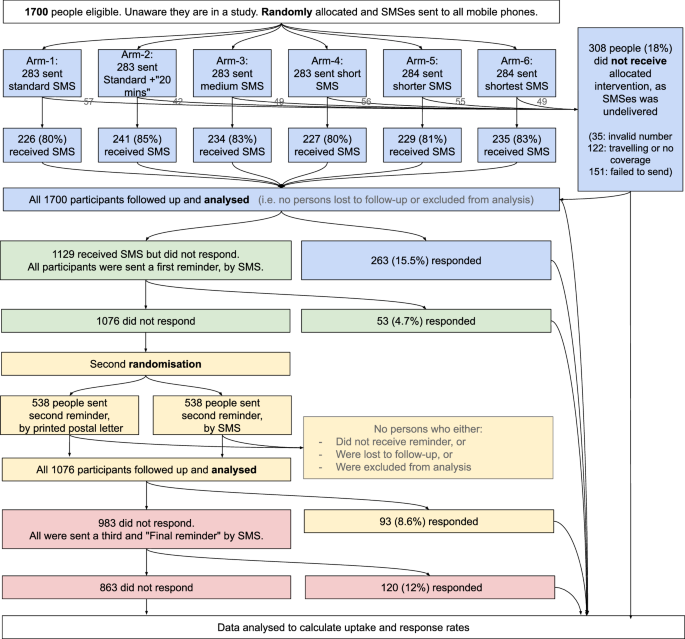
"Uptake varied significantly across different SMS reminder strategies, highlighting an increase from 12% with standard SMS to 20% with the shortest SMS, demonstrating the impact of communication length."
"The most effective reminder method proved to be postal reminders, achieving a +7% increase in uptake compared to +3% from SMS reminders, showcasing the value of multi-modal communication."
"Incorporating digital care into in-person services has the potential to boost screening uptake by 10%, raising total participation rates from 50% to 60%."
A study tested various SMS invitations to encourage participation in digital Health Checks among Londoners aged 40-74 without cardiovascular disease. The four-week study included 1700 individuals and utilized a six-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) design. The uptake rates varied, with the shortest SMS yielding a 20% response rate compared to 12% for the standard SMS. Multi-modal reminders, notably postal reminders, proved more effective, increasing participation substantially. Incorporating digital options into traditional services could enhance overall healthcare screening uptake.
#digital-screening #healthcare-uptake #randomized-controlled-trial #sms-reminders #mixed-modality-services
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]