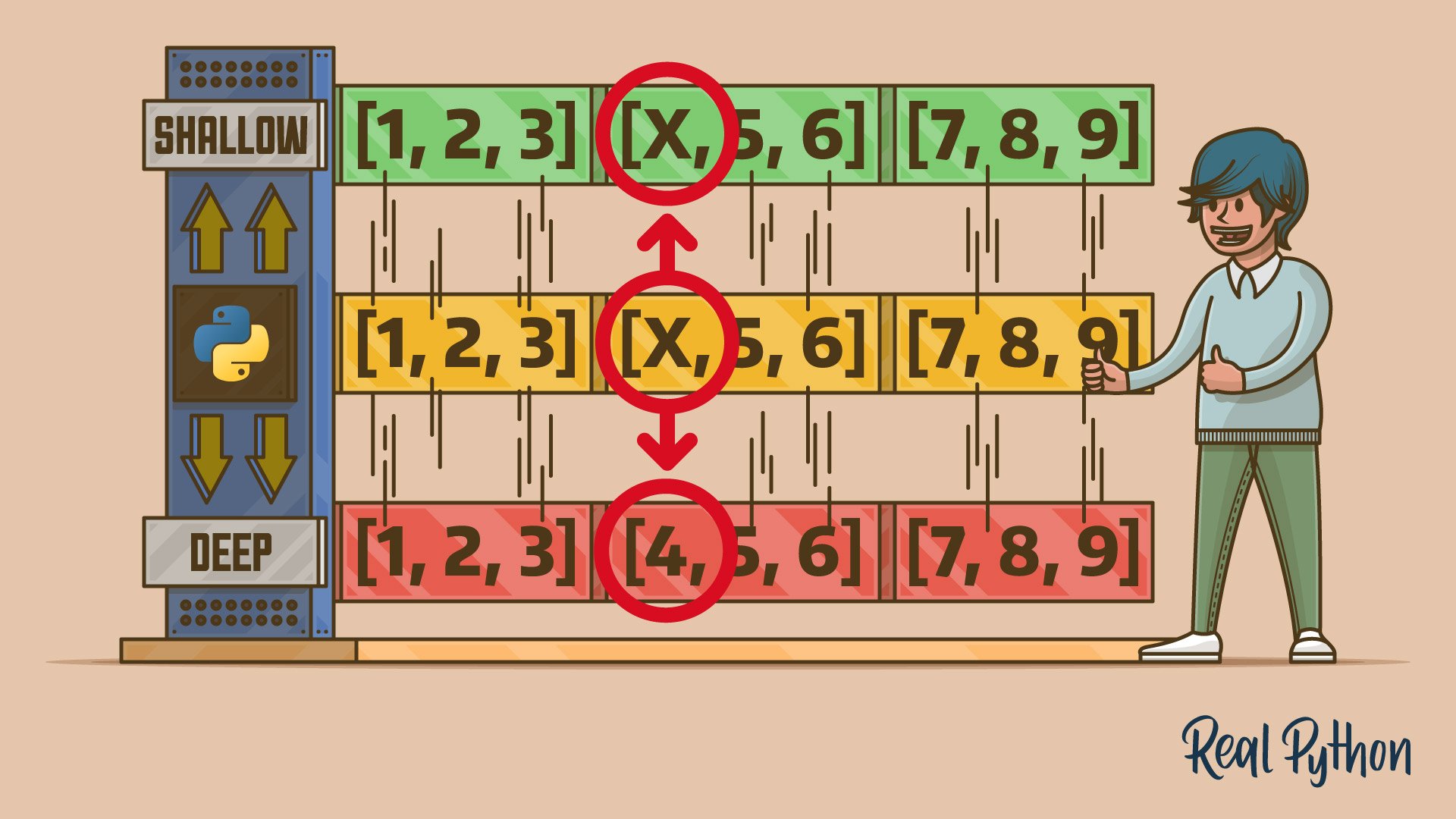
"Shallow copying creates a new object but references the same nested objects, leading to shared changes."
"Deep copying recursively duplicates all objects, ensuring full independence from the original."
"Python's copy module provides the copy() function for shallow copies and deepcopy() for deep copies."
"Custom classes can implement .__copy__() and .__deepcopy__() for specific copying behavior."
Copying objects in Python is crucial to prevent modifying original instances. Shallow copies create new objects while sharing references to nested objects, which allows changes to affect the originals. Deep copies, on the other hand, duplicate every object recursively, ensuring complete independence from the source. The built-in copy module in Python provides functions for both copying methods. Custom classes can define specific behavior for copying by implementing .__copy__() and .__deepcopy__(). Assignment does not create copies but simply binds variable names to existing objects.
Read at Realpython
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]