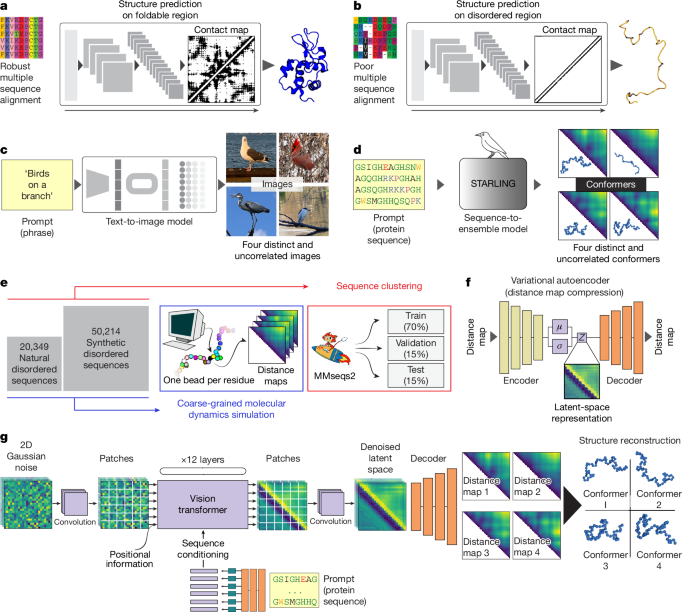
"Despite lacking a fixed structure, IDRs have key roles in essential cellular processes such as transcription, translation and cell signalling1. Owing to their broad structural heterogeneity, IDRs must be described by a conformational ensemble: a large collection of structurally distinct and interchanging conformations1. However, although IDRs cannot be represented as a single 3D structure, they do still possess sequence-encoded conformational biases, and ensembles can have essential roles in IDR function and may be perturbed in disease. Just as structural biology has been instrumental in understanding the molecular basis for folded domain function, there is a growing appreciation that the characterization of IDR ensembles may be important for understanding IDR function5,6."
"Various experimental techniques have been applied to interrogate sequence-ensemble relationships. Although these report on specific aspects of IDR ensembles, they fall short of providing a holistic description of the distribution of conformers (that is, the 3D coordinates of all residues in the protein across many different conformations, referred to here as a 'full structural ensemble'). To achieve this, the integration of computational modelling with experimental data has proven an effective route10,11,12,13."
"Conceptually, computational models and experiments can be combined in two different ways. One approach involves using physics-based models and reweighting or biasing towards experimental observables14,15. Another involves using experimental data to parameterize transferable force fields, which, in principle, do not require additional reweighting16. Although both approaches have been effective in providing insight into IDR behaviour, they require deep technical expertise to ensure reliable conclusions are drawn, and can also be computationally expensive."
Intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) constitute about 30% of eukaryotic proteomes and lack fixed tertiary structure while performing essential roles in transcription, translation and cell signalling. IDRs adopt conformational ensembles—large collections of interconverting structures—with sequence-encoded biases that influence function and can be altered in disease. Experimental methods probe specific ensemble features but do not yield full structural ensembles describing all residue coordinates across conformations. Integrating computational modelling with experimental data enables fuller ensemble characterization. Two main integration strategies exist: reweighting physics-based simulations toward observables, or parameterizing transferable force fields from experimental data; both require expertise and computational resources.
#intrinsically-disordered-regions #conformational-ensembles #integrative-modelling #force-field-parameterization
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]