"The engineering team at Cloudflare transitioned Quicksilver to a tiered caching architecture, improving storage efficiency while preserving consistency guarantees and low-latency reads."
"Quicksilver V1 stored all data on each server globally, leading to unmanageable disk space usage as the dataset grew, prompting the development of Quicksilver V2."
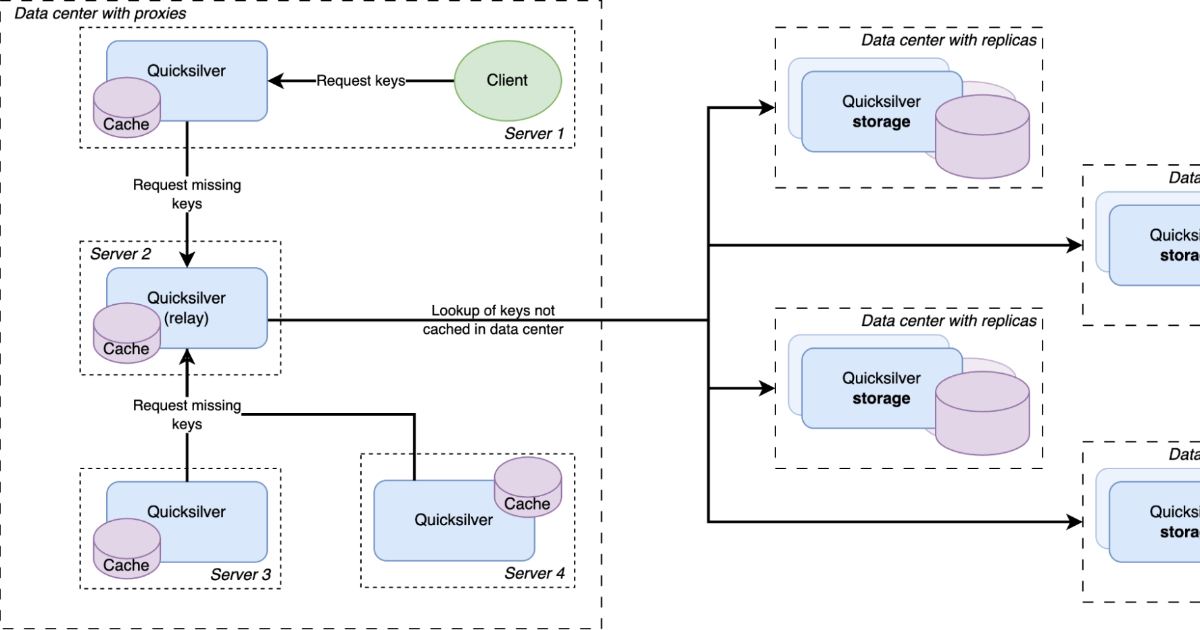
"The latest Quicksilver V2 features a multi-level caching strategy with local per-server caches, data center-wide sharded caches, and replicas on specialized storage nodes."
"Cloudflare's incremental journey from Quicksilver V1 to V2 involved migrating hundreds of thousands of live databases while managing billions of requests per second."
Cloudflare transitioned its key-value store, Quicksilver, from a model where all data was stored on every server to a tiered caching architecture. This evolution, from Quicksilver V1 to V2, improved storage efficiency and maintained consistency and low-latency operations. The initial system was unsustainable due to explosive data growth, leading to the introduction of a multi-level caching strategy in V2. This new architecture featured local caches, sharded caches across data centers, and full dataset replicas, addressing memory usage and cold cache challenges through persistent storage solutions.
Read at InfoQ
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]