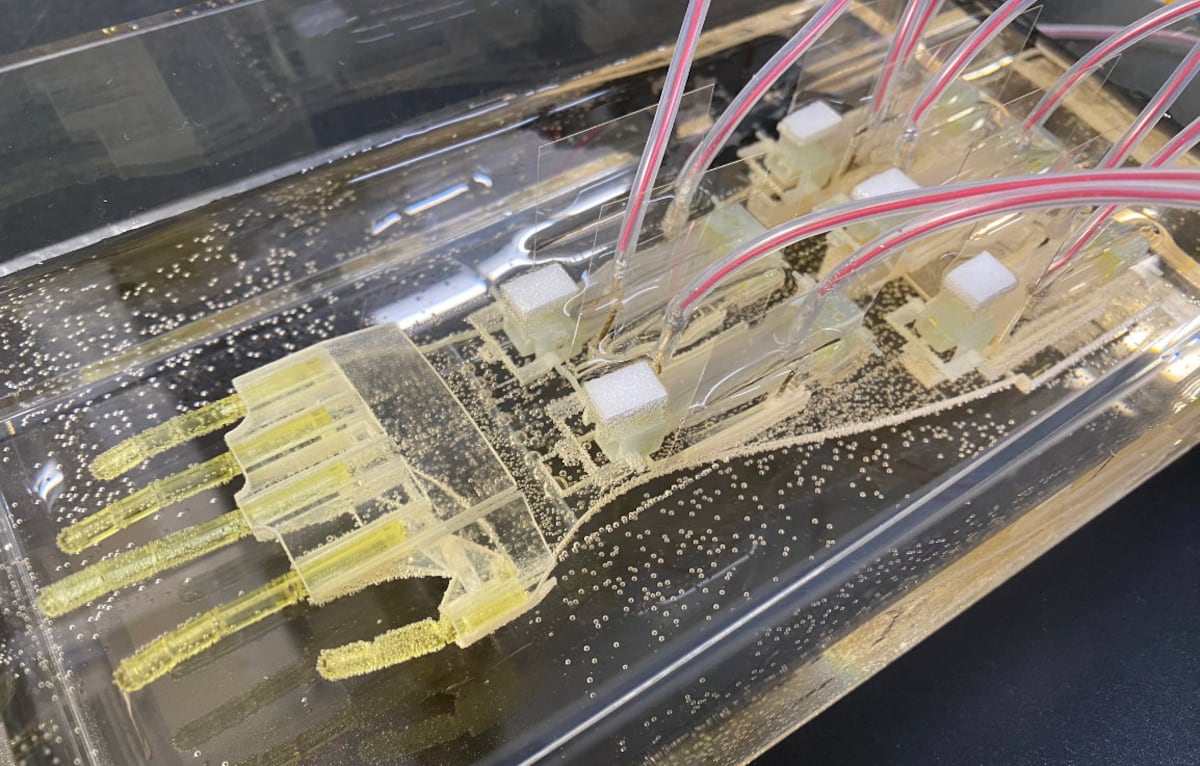
"Each MuMuTA is aimed at replicating muscle motion, which requires fine balance between muscle mass for strength and thinness for nutrient delivery. This innovation could revolutionize prosthetics."
"Takeuchi emphasizes that achieving muscle mass without compromising nutrient supply was critical, leading to the sushi roll design for multi-joint muscle based systems that support motion."
Aiming to merge technology with biology, recent bioengineering advancements include developing prosthetics that mimic natural body movement and self-regenerate using patients' cells. Researchers from the University of Tokyo and Waseda University created a significant 18-centimeter arm from human muscle tissue with functional fingers. At the same time, IBEC in Barcelona is using 3D bioprinting to emulate muscle structures. These innovations have promising applications in prosthetics, muscle tissue drug testing, and soft robotics, as noted by Professor Takeuchi, who highlights the technical challenges of achieving balance in muscle structure and force generation.
Read at english.elpais.com
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]