"Traditional physicalism insists that everything deemed 'real' must ultimately be reducible to the principles of physics and chemistry, leaving no room for the supernatural."
"Liberal naturalism embraces natural explanations while acknowledging that human experiences are genuinely real, providing a more inclusive view of reality that recognizes subjective experiences."
"Extended naturalism aims to unify objective science with subjective experience, providing a cohesive natural worldview that integrates both scientific understanding and human consciousness."
"Naturalism, as a philosophical stance, emphasizes that all phenomena originate from natural properties and causes, grounding knowledge in the empirical methods and principles of the natural sciences."
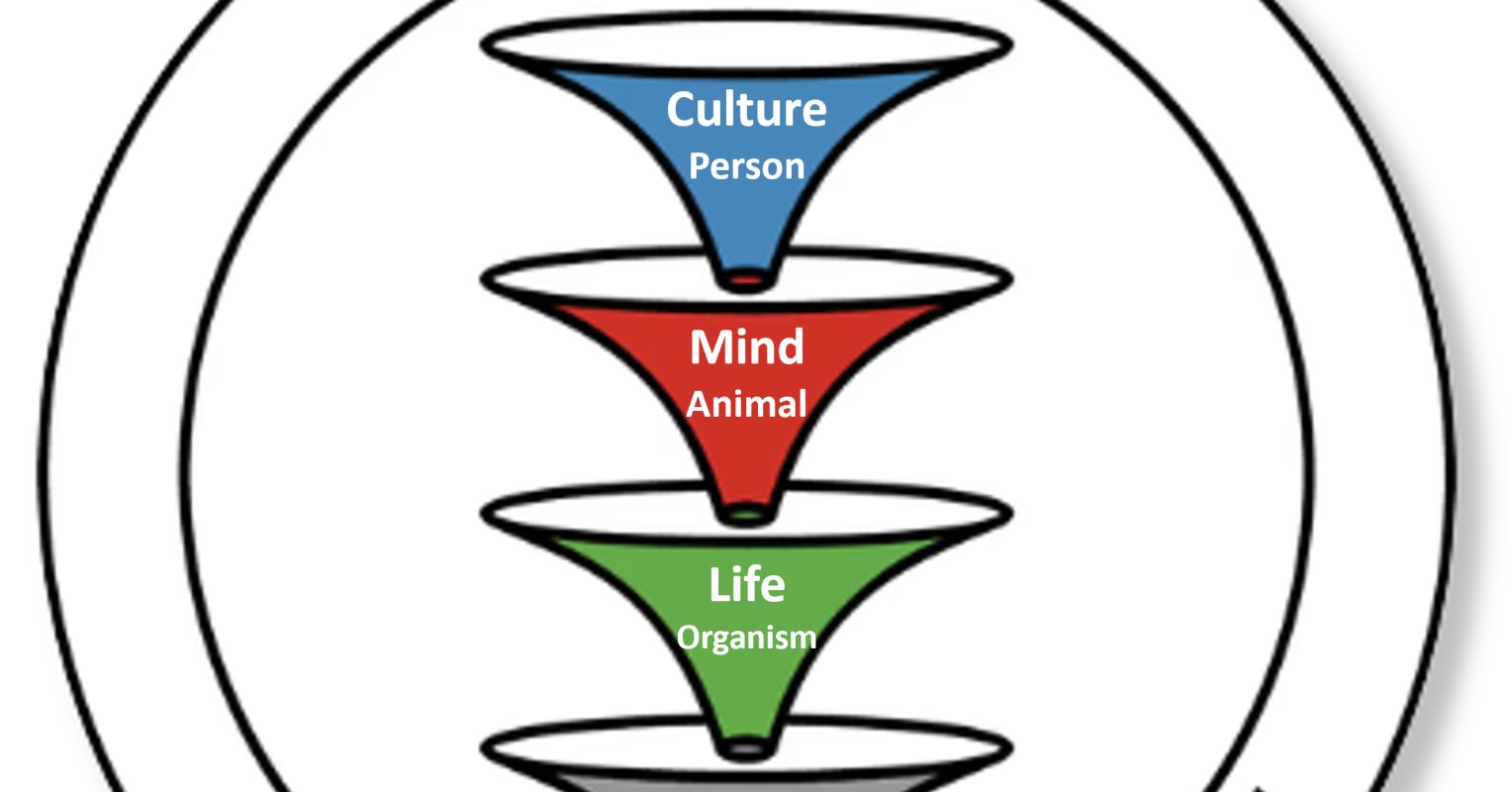
Naturalism is a philosophical view emphasizing that all phenomena arise from natural properties and causes, dismissing supernatural elements. It evolved from natural philosophy, which once distinguished between the natural and supernatural realms. As the natural sciences developed, skepticism towards the supernatural grew, leading to a unified understanding of reality as primarily natural. Within this framework, various interpretations exist regarding the nature of 'natural' and how to comprehend human experiences, ethics, and complexities of consciousness, particularly in the context of objective science versus subjective experience.
Read at Psychology Today
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]