Artificial intelligence
fromInfoQ
4 weeks agoGoogle Releases Gemma 3 270M Variant Optimized for Function Calling on Mobile and Edge Devices
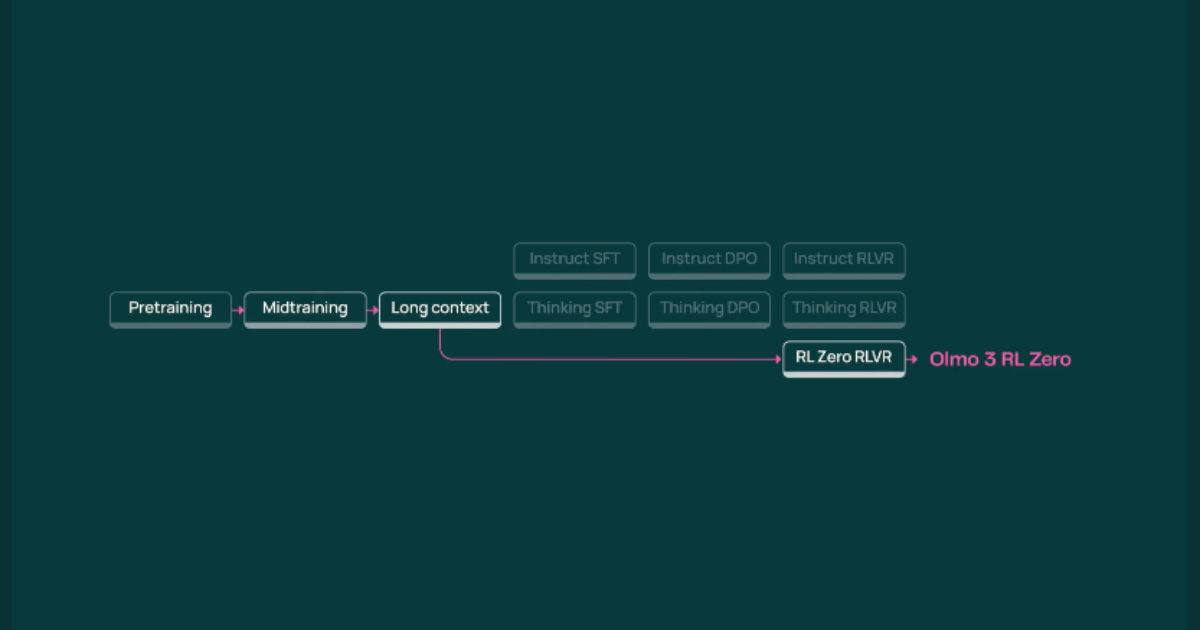
FunctionGemma is a lightweight, fine-tuned Gemma 3 270M variant that translates natural language into structured function and API calls for efficient on-device agent execution.