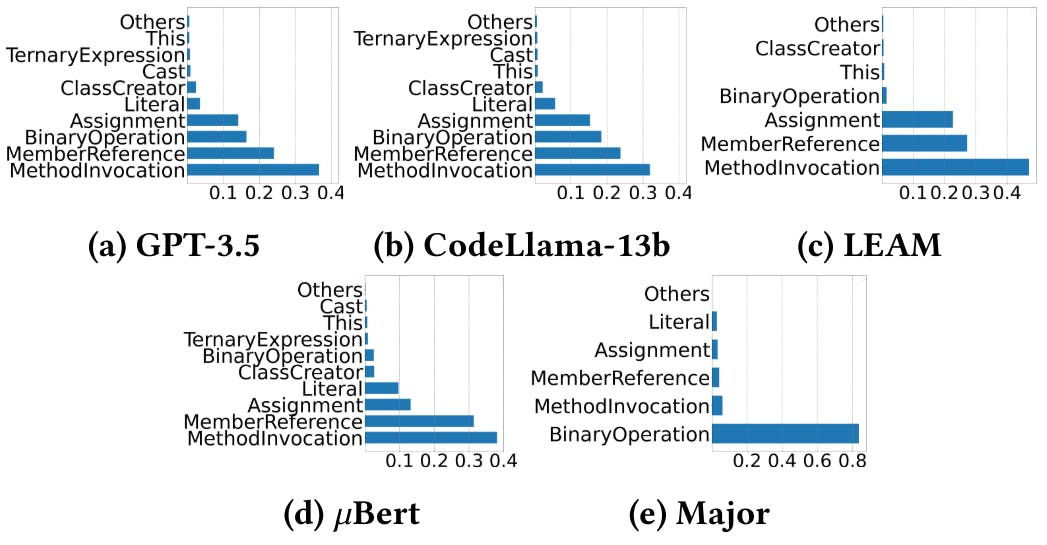
"The performance of closed-source LLMs typically exceeds that of open-source models in key metrics, emphasizing the importance of training data quality and model architecture."
"GPT-3.5 is optimal for mutation generation due to its rapid generation capabilities, while GPT-4 shines in usability and behavior similarity metrics."
The article investigates the performance of various large language models (LLMs) in generating code mutations, focusing on usability, behavior similarity, and generation costs. Results reveal closed-source models like GPT-4 outperform open-source alternatives in usability and behavior metrics, while GPT-3.5 excels in rapid mutation generation. Additionally, model architecture and training data quality significantly influence performance, with deeper insights into non-compilable mutations uncovering critical root causes. The study underscores the complex trade-offs between cost, usability, and performance in code-related tasks using LLMs.
Read at Hackernoon
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]