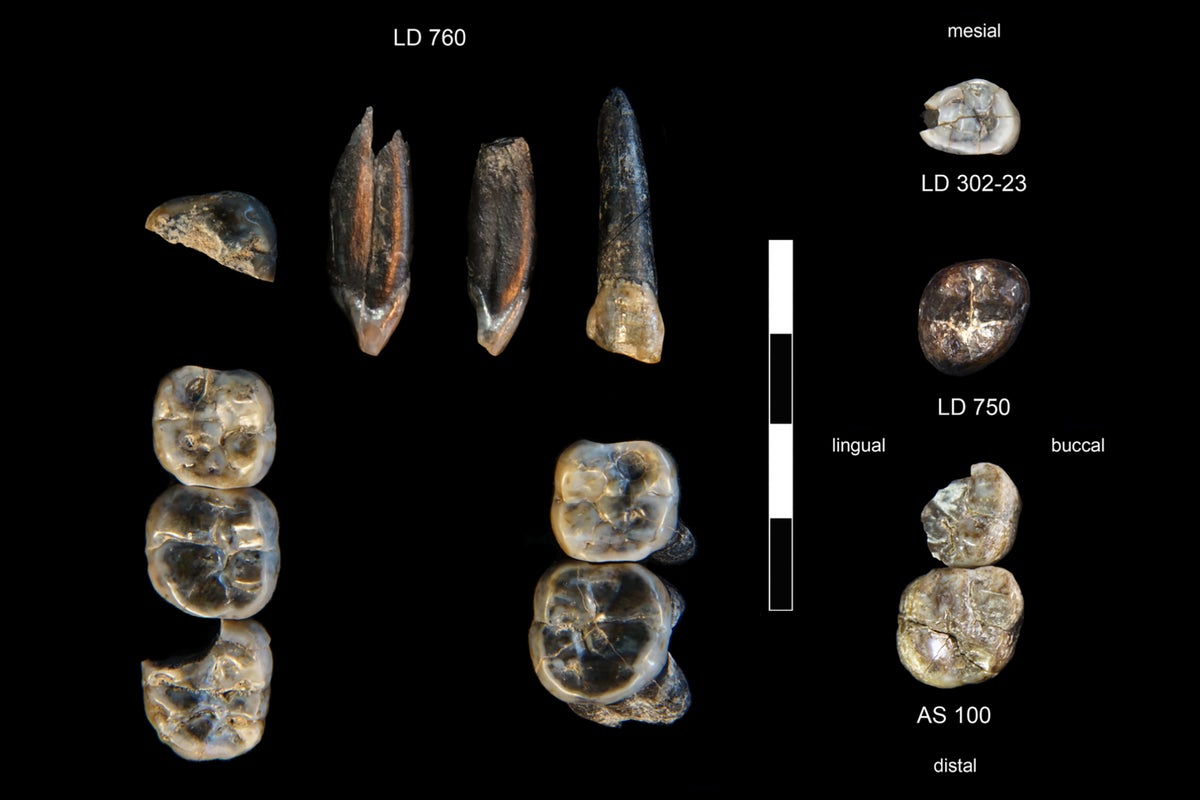
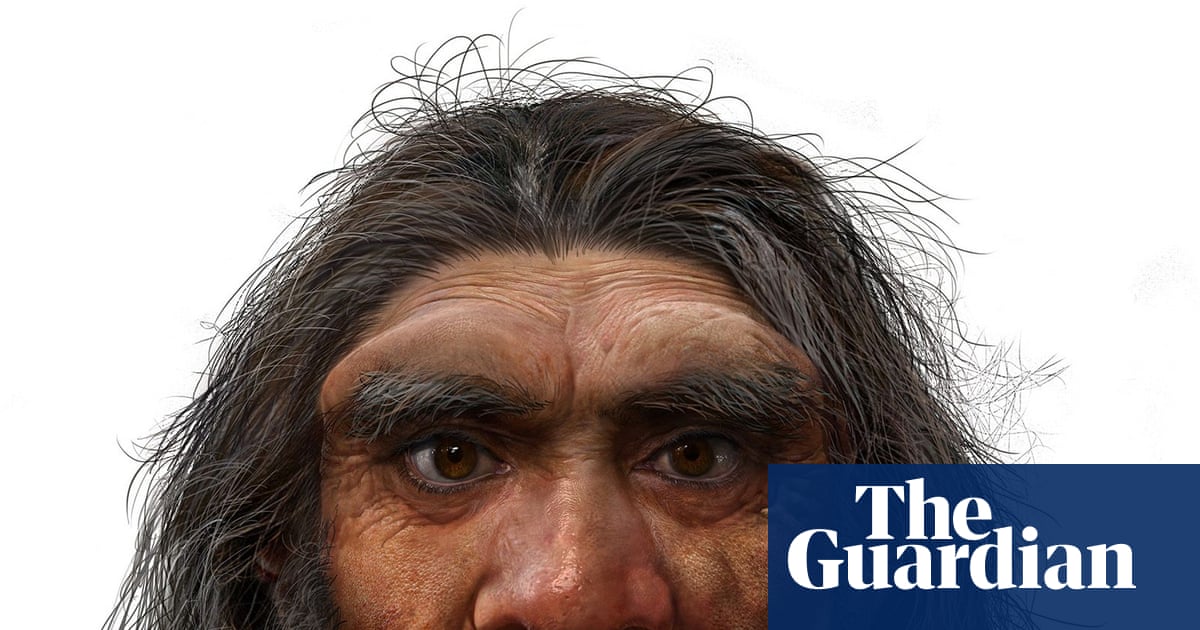
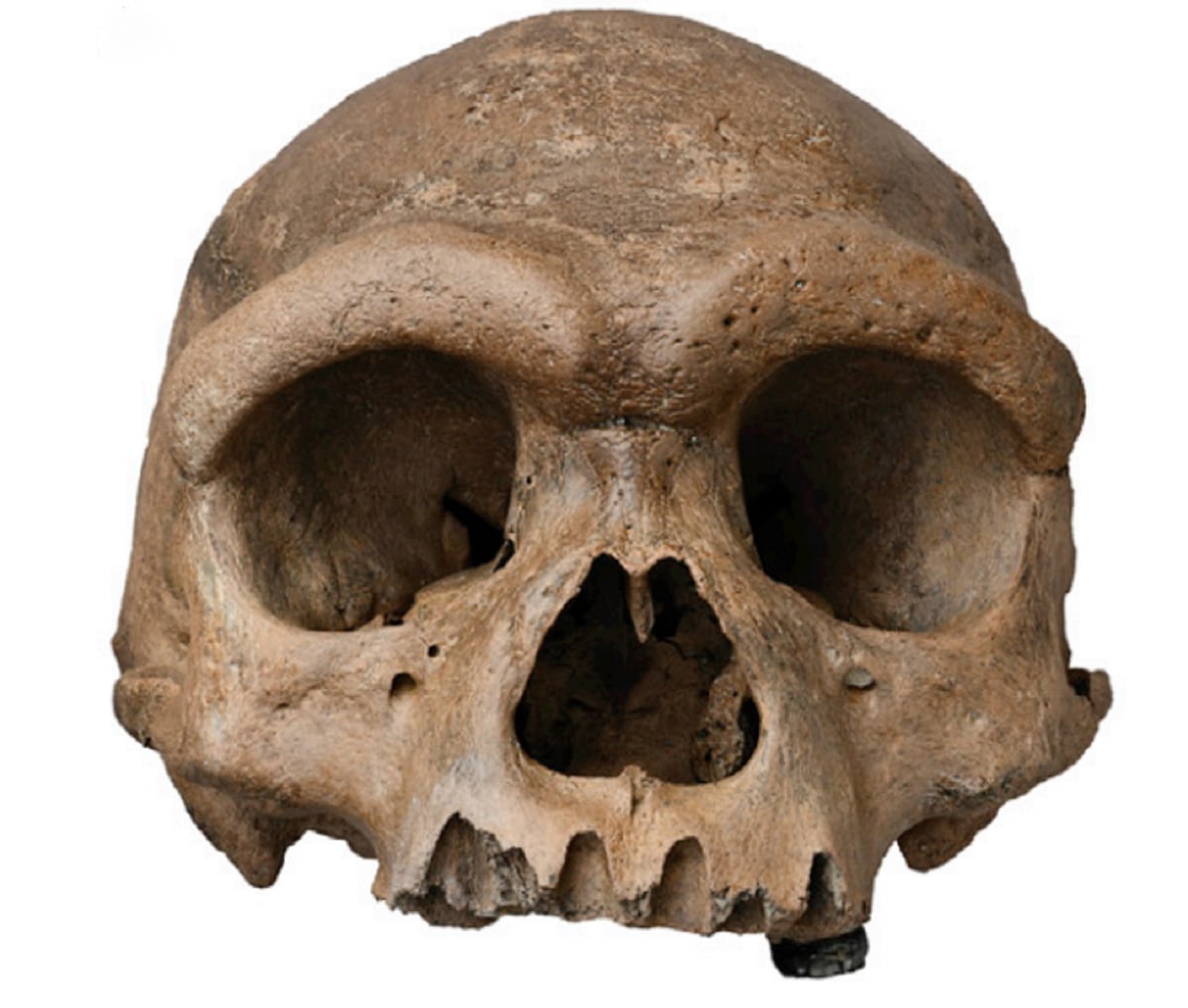
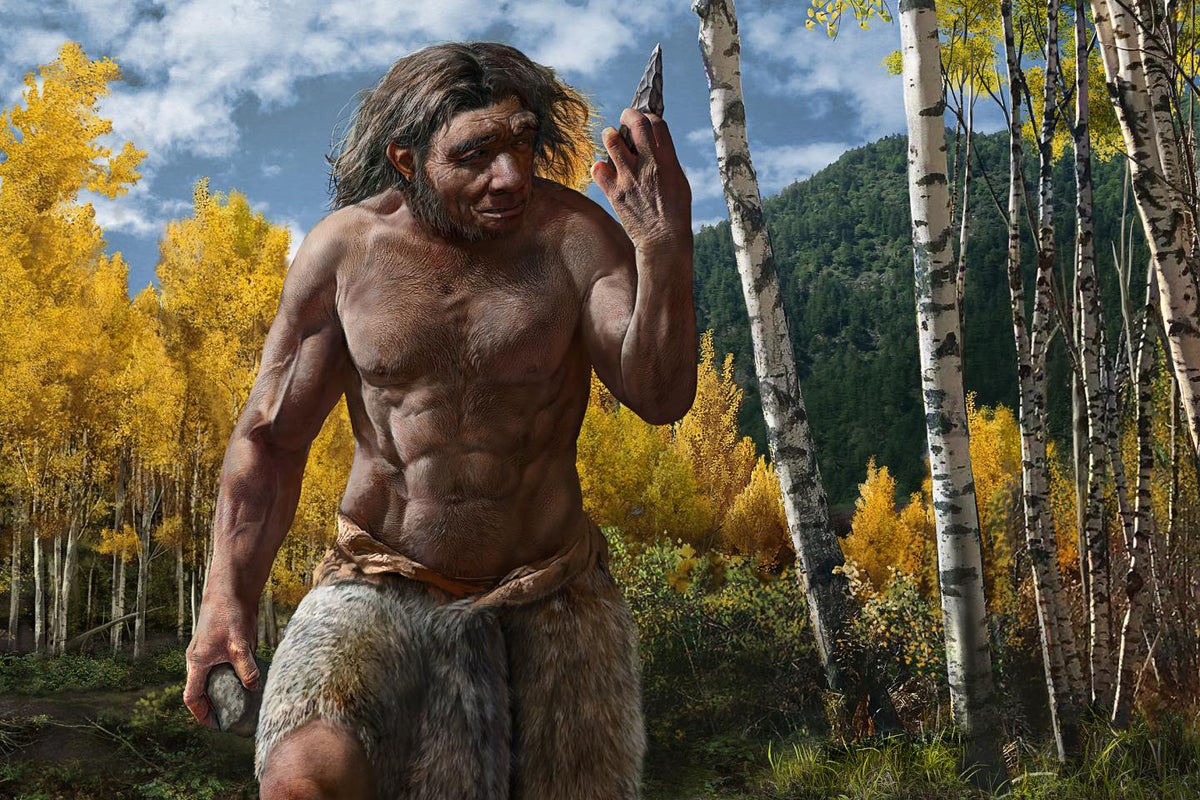
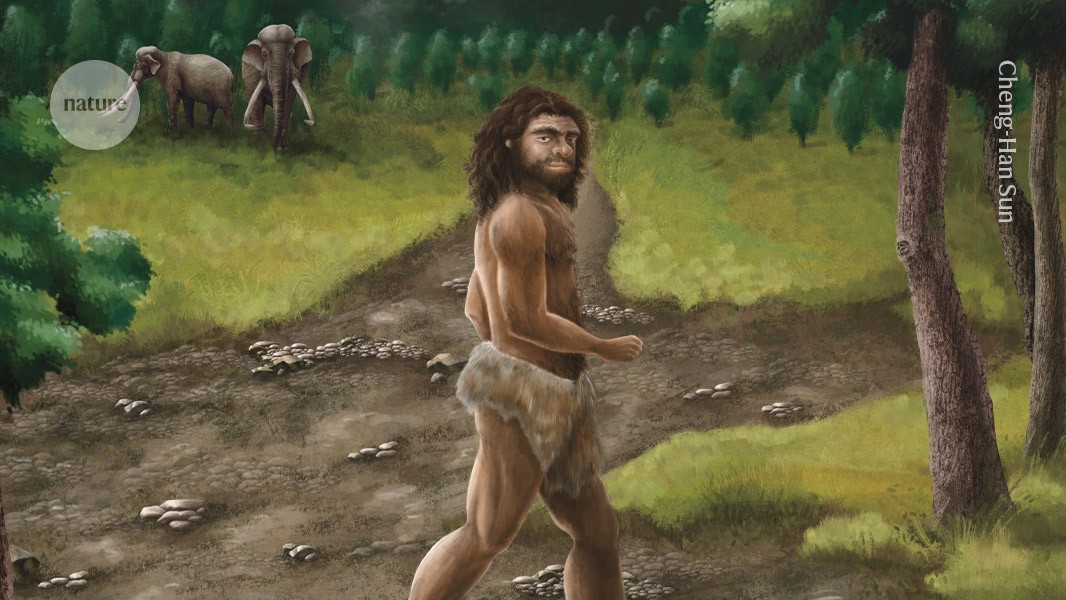
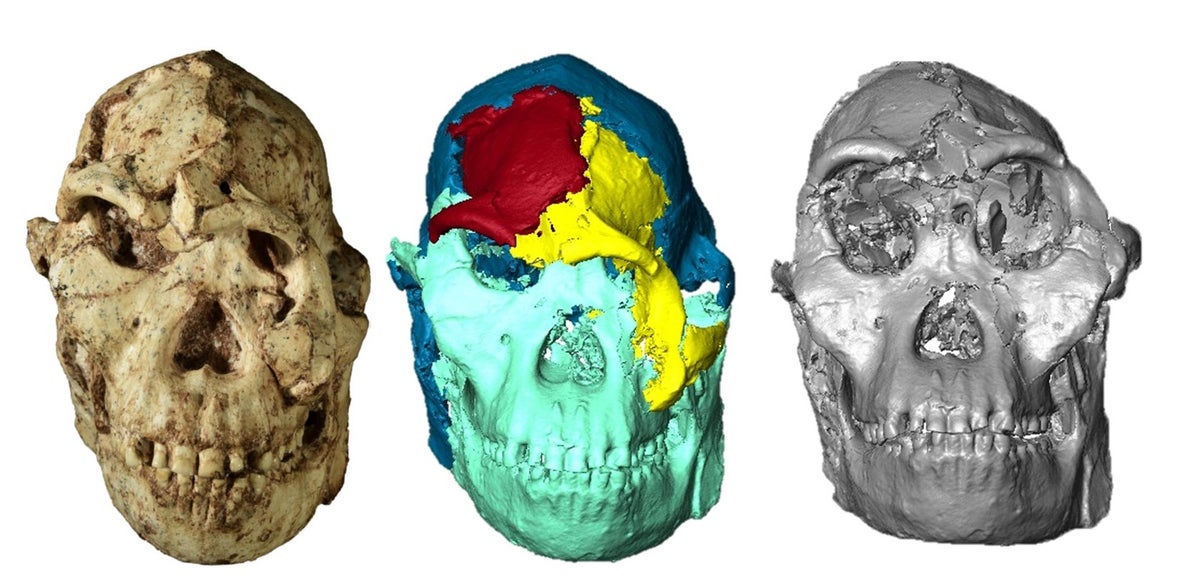
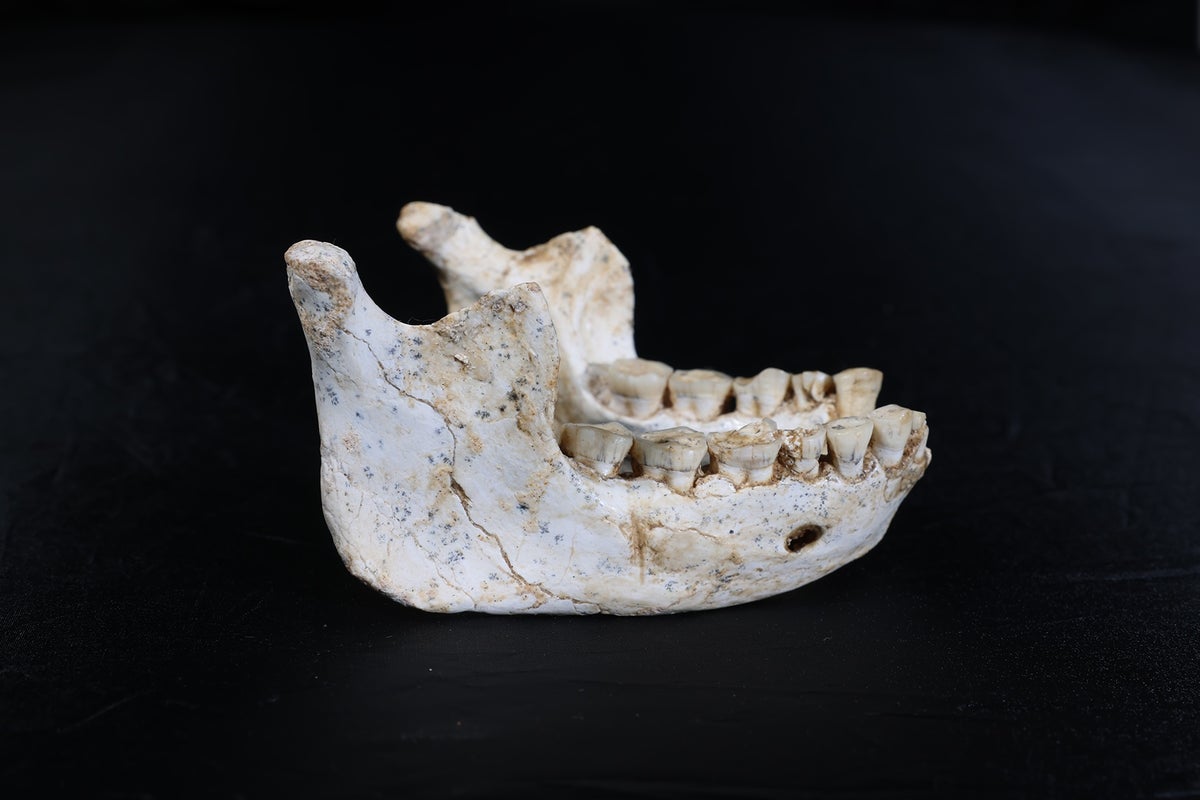
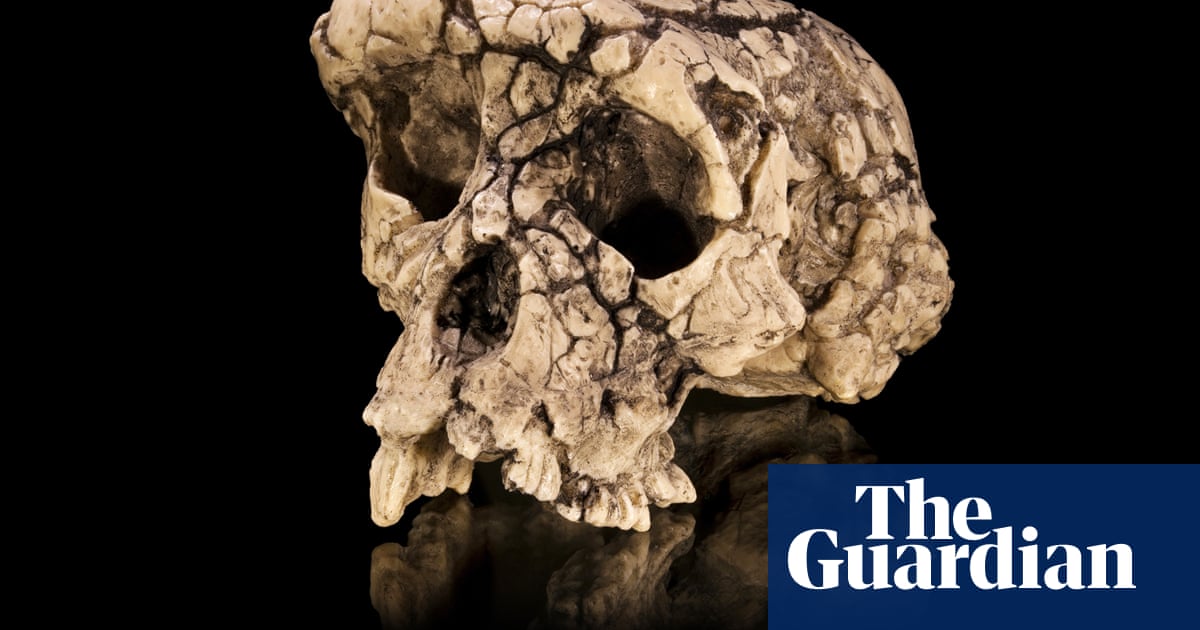
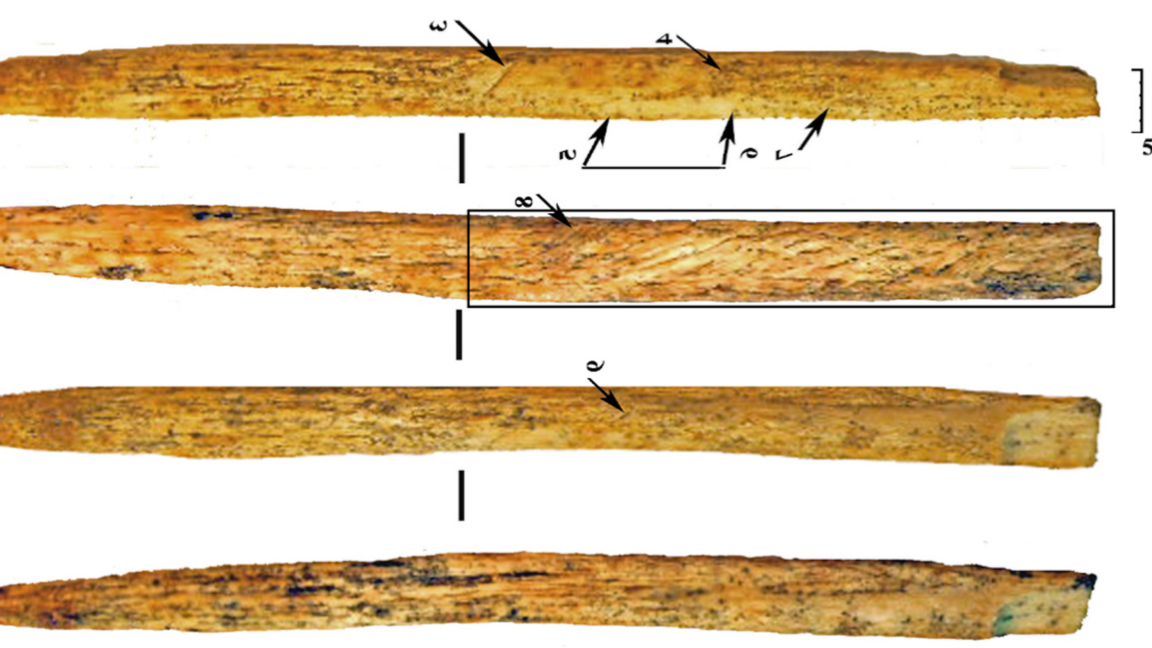
Wine
fromwww.npr.org
2 days agoHumans' pull toward alcohol may have ancient origins (according to chimp pee)
Wild African chimpanzees consume alcohol from fermented fruit, suggesting human attraction to alcohol has ancient evolutionary origins rooted in seeking calorie-rich food sources.